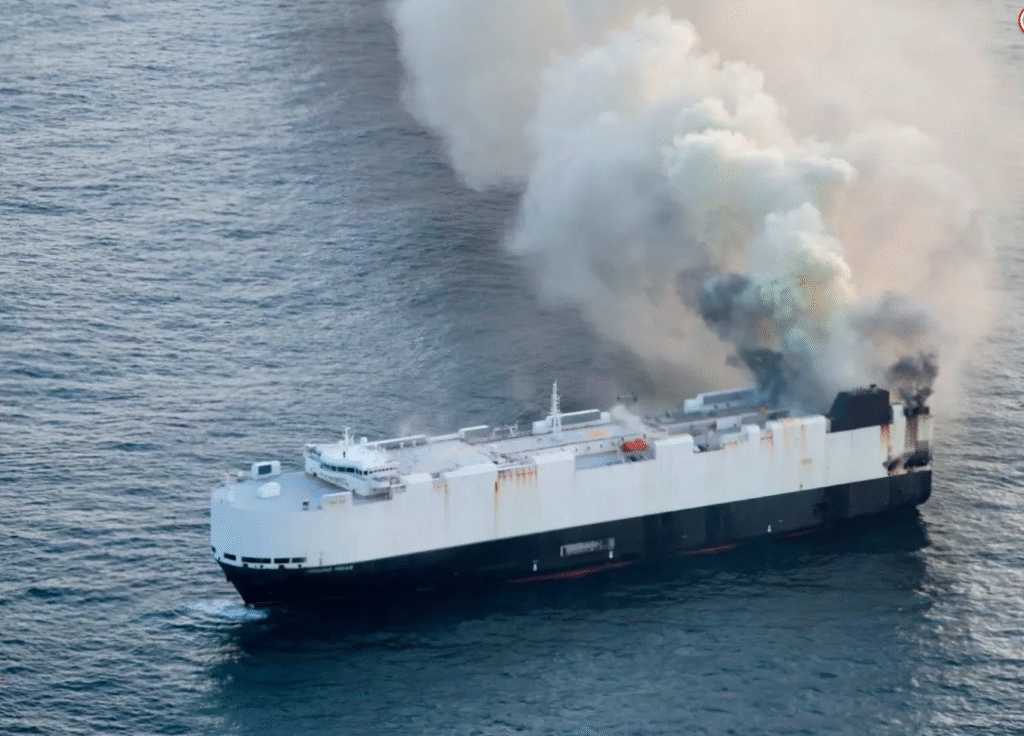
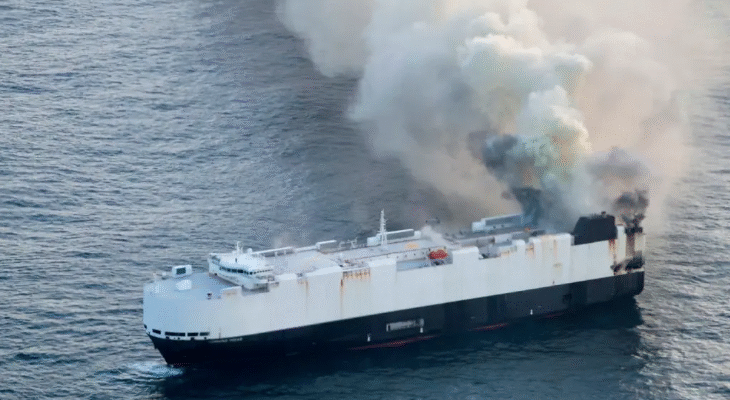
A large cargo ship transporting thousands of vehicles, including electric vehicles (EVs), recently sank in the Pacific Ocean following a devastating fire onboard. The incident has raised significant environmental and safety concerns worldwide, particularly regarding the handling and potential risks associated with lithium-ion batteries found in EVs. As global demand for electric vehicles surges, the event has spotlighted the challenges of safely transporting these high-tech cars across oceans.
The Incident: Fire and Sinking in the Pacific
The cargo ship, operated by a major international shipping company, was en route from East Asia to North America when a fire broke out in one of its vehicle decks. The blaze reportedly started in the early hours of the voyage, quickly spreading through the densely packed rows of cars.
Despite the crew’s efforts to contain the fire, the flames intensified, forcing an emergency evacuation of all personnel. After burning for several hours, the ship’s structural integrity was compromised, leading to its eventual sinking hundreds of miles offshore in the Pacific.
Authorities coordinated a large-scale rescue and containment operation, focusing on minimizing environmental damage and recovering survivors. Fortunately, all crew members were rescued without casualties, but the sinking of the vessel carrying thousands of vehicles—including a substantial number of electric cars—has stirred concern globally.
The Scale of the Loss: Thousands of Cars at Sea

Reports estimate that the ship was carrying approximately 5,000 vehicles, ranging from conventional gasoline-powered cars to a growing share of electric models from various manufacturers. The shipping of EVs overseas has become increasingly common as automakers ramp up production to meet expanding markets.
The sheer number of vehicles lost at sea represents a significant economic blow to manufacturers, distributors, and insurers. However, the sinking also raises pressing environmental questions, particularly related to the potential hazards posed by submerged lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles.
EV Batteries: What’s the Concern?
Electric vehicles are powered by lithium-ion batteries, which store vast amounts of energy in compact, lightweight units. While these batteries have revolutionized the auto industry by enabling zero-emission transportation, they pose unique challenges when damaged or exposed to extreme conditions.
Fire Risk
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their energy density, but they can be volatile if punctured, overheated, or short-circuited. Thermal runaway, a chain reaction leading to uncontrollable heat and fire, can occur, as was reportedly the case in the initial blaze onboard the ship.
Once a lithium-ion battery ignites, extinguishing the fire can be difficult due to the chemical reactions involved. This risk complicates firefighting efforts, especially in confined, metal-rich environments like a ship’s vehicle deck.
Environmental Impact
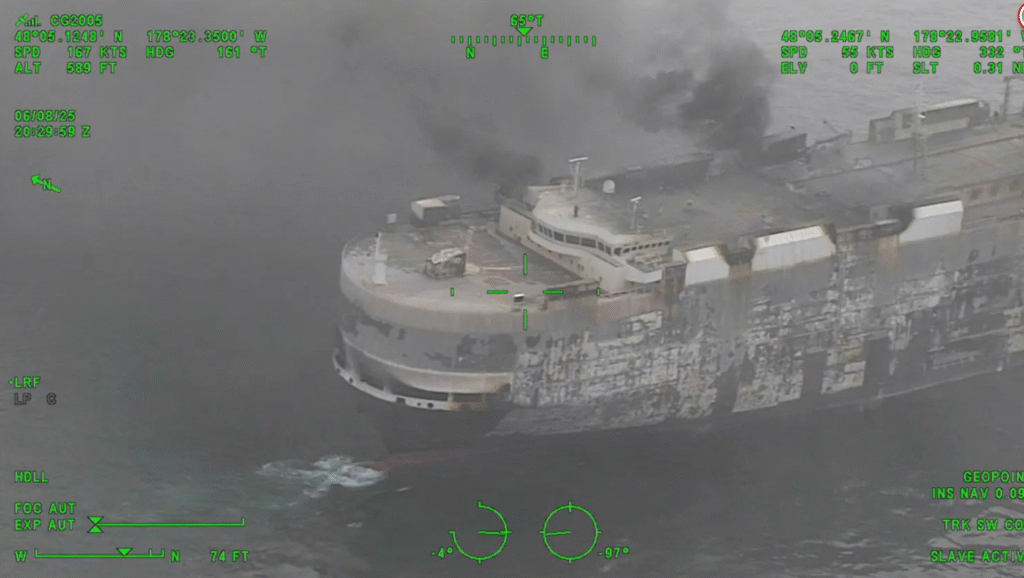

The sinking of vehicles containing lithium-ion batteries introduces concerns about battery leakage and contamination. When submerged, damaged batteries may release toxic chemicals such as lithium salts, heavy metals like cobalt and nickel, and organic electrolytes into the marine environment.
These substances pose threats to aquatic life and ecosystems, with unknown long-term consequences. The Pacific Ocean, a vast and biodiverse body of water, could be impacted by the gradual release of these toxic compounds as the vehicles corrode underwater.
Disposal and Recovery Challenges
Recovering sunken vehicles, especially electric ones, is a daunting task. Salvage operations underwater are expensive and dangerous, made more complex by the potential instability of damaged batteries. If the vehicles remain on the ocean floor, ongoing corrosion may worsen environmental contamination.
Furthermore, safe disposal of damaged EV batteries recovered from the sea is a logistical and technological challenge. Specialized recycling processes are needed to handle hazardous materials and recover valuable metals without causing further harm.
Industry and Regulatory Responses
The sinking has triggered urgent discussions within shipping, automotive, and environmental regulatory communities about the safe transport of electric vehicles.
Shipping Industry

Shipping companies are reevaluating fire safety protocols, cargo storage methods, and emergency response measures to better handle the unique risks of EV batteries onboard vessels. Some experts suggest enhanced fire suppression systems, improved battery monitoring during transit, and stricter packaging regulations.
Additionally, there is a push for clearer guidelines on segregating EVs from other cargo, as well as better training for crews in handling battery fires.
Automotive Manufacturers
Car makers are collaborating with shippers and regulators to develop safer battery technologies and packaging solutions that reduce fire risk during transport. Innovations include battery enclosures with improved thermal management and impact resistance.
The incident also spotlights the need for transparent communication about battery safety features and risks throughout the supply chain.
Environmental Agencies

Governments and environmental organizations are calling for comprehensive impact assessments of the sinking, including marine pollution monitoring and potential remediation efforts.
International maritime bodies may consider revising shipping regulations to address emerging hazards from electric vehicle transport more explicitly.
Broader Implications for the EV Market

The accident serves as a reminder that while electric vehicles offer significant environmental benefits over fossil fuel-powered cars, their production, transportation, and disposal come with complex challenges.
As global EV adoption accelerates—projected to reach millions of vehicles annually—stakeholders must develop robust systems to manage risks at every stage, from manufacturing and shipping to end-of-life recycling.
This event may prompt industry-wide investments in safer battery chemistries, more rigorous shipping standards, and enhanced emergency response capabilities. It also underscores the importance of international cooperation in regulating new technologies with global supply chains.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of EV Transport
The sinking of a cargo ship carrying thousands of vehicles, including electric cars, after a devastating fire in the Pacific Ocean is a stark illustration of the challenges facing modern logistics and environmental stewardship.
While no human lives were lost, the environmental risks associated with submerged lithium-ion batteries demand careful attention and action. This incident highlights the urgent need for safer battery technologies, improved shipping safety standards, and stronger environmental protections.
As electric vehicles continue transforming the automotive landscape, the world must ensure that the systems supporting this transition are equally advanced and resilient—minimizing risks while maximizing the benefits of a cleaner, more sustainable future.
Video Read news information |